#Open-Source Data Recovery Software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Data Recovery Software
Data recovery software is a type of software designed to retrieve lost or deleted data from storage devices such as hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), USB drives, memory cards, and more. This software is particularly useful in situations where data has been accidentally deleted, corrupted, or lost due to various reasons like hardware failures, virus attacks, or formatting errors. Here are…

View On WordPress
#Commercial Data Recovery Software#Common Data Loss#EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard#Free Data Recovery Software#MiniTool Power Data Recovery#Open-Source Data Recovery Software#Recovery Options#Recuva#Stellar Data Recovery#TestDisk (Open source)
0 notes
Text
Top 10 Open Source NAS software in 2023
Top 10 Open Source NAS software in 2023 #homelab #selfhosted #opensourceNASsolutions #freeNASsoftware #networkattachedstorage #NASserverhardware #datastoragesolutions #selfhostedNASbenefits #personalcloudserver #filesharingprotocols
There are many freely available open-source NAS solutions you can download for free. An open-source NAS server offers an excellent way to manage and protect your data. Let’s dive deeper into the top free NAS software solutions available in 2023. Network attached storage nas for home Table of contentsIntroduction to Open Source NAS SolutionsTrueNAS Scale and TrueNAS Core: Great Open Source…

View On WordPress
#data backup and recovery#data integrity and security#data storage solutions#file sharing protocols#free NAS software#NAS server hardware#network attached storage#open source NAS solutions#personal cloud server#self-hosted NAS benefits
0 notes
Text
Free software recommendations for various things:
LibreOffice - A full home office suite comparable to Microsoft Office. Easy to use and you can choose the UI layout from several types; it can handle docx and other Microsoft Office document formats; it still does not include AI unless you specifically add that extension on purpose, so unlike other office suites it's not shoving AI down your throat.
Calibre - Ebook manager bundled with an ebook editor and ereader software. It can follow news feeds, downloading them into epub format. Convert ebooks from one format into (many) others. Run a server to make access your books from different computers/phones/tablets easier. And so much more... without even touching on the additional functionality that plugins can add. With plugins it can be used for DRM stripping (which can still remove DRM from even Kindle ebooks, if you have a kindle that you can download the ebook to and use to transfer to your computer). It can also handle downloading fanfics and their metadata using the FanFicFare plugin. (Which I've written tutorials about.) There are officially supported plugins (like FanFicFare) that are easy to install and unofficial plugins (like the DRM stripper) that take more work, so it's extremely customizable.
Syncthing - Want to host your own local file backup system? Have an old laptop that you can reformat with a linux distro? And maybe a spare hard drive? Perfect, you have what you need to set up a home file backup system. Reformat the computer with the new operating system, install syncthing on that computer and on the computer you want to back up files for and the two installations of the software can sync over your home network. Put it on your phone and back up your photos. The software is open source, encrypted, and you can turn it off so that your computer (or phone) is only running it on a trusted network. You control where the synced data lives, which computers on your network those synced folders are shared with (allowing for sharing between multiple computers) and even what type of file backups happen if data is, say, accidentally deleted. (File recovery!!!)
Plex or Emby - Both are free to install on any computer, point at any movie/tv show/audiobook/music files you've got sitting around, and bam you've got a home media streaming server. Both have paid tiers for more features (including tv tuner integration to act as a DVR), but what they can do for free is already impressive and well handled. Both have easy to use UI and it largely comes down to personal preference as to one is better than the other.
Notepad++ - A notepad type program that can also serve as a decent lightweight code editor. I use it for noodling around with code scripts and snippets, writing lists, and various other small tasks. It's not something I'd use for my professional code writing but it's great for just messing around with something on my own time.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
5 IT Cost Saving Strategies for Your Enterprise Infrastructure
Managing enterprise IT infrastructure is a balancing act between performance, reliability, and cost. As technology evolves rapidly, so do expenses. To stay competitive and efficient, IT managers must find smart ways to reduce costs without compromising service quality or security. Below are five proven IT cost-saving strategies that can make a meaningful impact on your enterprise infrastructure.
1. Extend the Life of Existing Hardware
Rather than defaulting to frequent hardware refresh cycles, enterprises can often extend the life of servers, storage devices, and networking hardware through proper maintenance and strategic upgrades. Partnering with a third-party maintenance provider for post-warranty support can reduce costs by 30-70% compared to OEM contracts.
💡 Tip: Use asset lifecycle management tools to monitor hardware health and optimize replacement timing based on performance, not just age.
2. Leverage Cloud and Hybrid Infrastructure
Moving specific workloads to the cloud—or adopting a hybrid cloud model—can reduce the cost of owning and maintaining physical infrastructure. Cloud services provide flexibility and scalability, allowing you to pay only for what you use.
💡 Tip: Use cloud cost optimization tools to avoid waste, identify underutilized instances, and right-size your resources.
3. Optimize Software Licensing
Licensing costs can quietly eat into IT budgets. Regular audits of software usage can help identify unused or underutilized licenses, especially with large suites or per-user subscription models.
💡 Tip: Consider switching to open-source or lower-cost alternatives for certain tools, and negotiate volume discounts or enterprise agreements with vendors.
4. Consolidate and Virtualize Resources
Server consolidation through virtualization reduces the need for physical hardware, power, and cooling. It also simplifies management, backup, and disaster recovery planning.
💡 Tip: Evaluate opportunities for workload consolidation across departments and assess whether underused servers can be decommissioned or repurposed.
5. Implement Preventive Maintenance and Monitoring
Downtime is costly. By implementing proactive monitoring tools and a preventive maintenance strategy, you can catch performance issues before they lead to outages or data loss—saving both money and reputation.
💡 Tip: Schedule regular health checks for your servers and storage systems, and set up alerts for threshold-based issues like CPU spikes or disk failure warnings.
Final Thoughts
Cost optimization isn’t about cutting corners—it’s about making smarter, data-driven decisions. With the right strategies, enterprises can lower IT infrastructure costs while improving agility, performance, and reliability. Evaluate your current infrastructure and consider where these strategies can have the most immediate impact.

0 notes
Text
DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management
In this "DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management," we will explore the fundamental concepts of DBMS, its importance, and how you can get started with managing data effectively.
What is a DBMS?
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a software tool that facilitates the creation, manipulation, and administration of databases. It provides an interface for users to interact with the data stored in a database, allowing them to perform various operations such as querying, updating, and managing data. DBMS can be classified into several types, including:
Hierarchical DBMS: Organizes data in a tree-like structure, where each record has a single parent and can have multiple children.
Network DBMS: Similar to hierarchical DBMS but allows more complex relationships between records, enabling many-to-many relationships.
Relational DBMS (RDBMS): The most widely used type, which organizes data into tables (relations) that can be linked through common fields. Examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
Object-oriented DBMS: Stores data in the form of objects, similar to object-oriented programming concepts.
Why is DBMS Important?
Data Integrity: DBMS ensures the accuracy and consistency of data through constraints and validation rules. This helps maintain data integrity and prevents anomalies.
Data Security: With built-in security features, DBMS allows administrators to control access to data, ensuring that only authorized users can view or modify sensitive information.
Data Redundancy Control: DBMS minimizes data redundancy by storing data in a centralized location, reducing the chances of data duplication and inconsistency.
Efficient Data Management: DBMS provides tools for data manipulation, making it easier for users to retrieve, update, and manage data efficiently.
Backup and Recovery: Most DBMS solutions come with backup and recovery features, ensuring that data can be restored in case of loss or corruption.
Getting Started with DBMS
To begin your journey with DBMS, you’ll need to familiarize yourself with some essential concepts and tools. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Understand Basic Database Concepts
Before diving into DBMS, it’s important to grasp some fundamental database concepts:
Database: A structured collection of data that is stored and accessed electronically.
Table: A collection of related data entries organized in rows and columns. Each table represents a specific entity (e.g., customers, orders).
Record: A single entry in a table, representing a specific instance of the entity.
Field: A specific attribute of a record, represented as a column in a table.
Step 2: Choose a DBMS
There are several DBMS options available, each with its own features and capabilities. For beginners, it’s advisable to start with a user-friendly relational database management system. Some popular choices include:
MySQL: An open-source RDBMS that is widely used for web applications.
PostgreSQL: A powerful open-source RDBMS known for its advanced features and compliance with SQL standards.
SQLite: A lightweight, serverless database that is easy to set up and ideal for small applications.
Step 3: Install the DBMS
Once you’ve chosen a DBMS, follow the installation instructions provided on the official website. Most DBMS solutions offer detailed documentation to guide you through the installation process.
Step 4: Create Your First Database
After installing the DBMS, you can create your first database. Here’s a simple example using MySQL:
Open the MySQL command line or a graphical interface like MySQL Workbench. Run the following command to create a new CREATE DATABASE my_first_database;
Use the database: USE my_first_database;
Step 5: Create Tables
Next, you’ll want to create tables to store your data. Here’s an example of creating a table for storing customer information:
CREATE TABLE customers ( 2 customer_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, 3 first_name VARCHAR(50), 4 last_name VARCHAR(50), 5 email VARCHAR(100), 6 created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP 7);
In this example, we define a table named customers with fields for customer ID, first name, last name, email, and the date the record was created.
Step 6: Insert Data
Now that you have a table, you can insert data into it. Here’s how to add a new customer:
1 INSERT INTO customers (first_name, last_name, email) 2VALUES ('John', 'Doe', '[email protected]');
Query Data
To retrieve data from your table, you can use the SELECT statement. For example, to get all customers:
1 SELECT * FROM customers;
You can also filter results using the WHERE clause:
SELECT * FROM customers WHERE last_name = 'Doe';
Step 8: Update and Delete Data
You can update existing records using the UPDATE statement:
UPDATE customers SET email = '[email protected]' WHERE customer_id = 1;
To delete a record, use the DELETE statement:
DELETE FROM customers WHERE customer_id = 1;
Conclusion
In this "DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management," we’ve explored the essential concepts of Database Management Systems and how to get started with managing data effectively. By understanding the importance of DBMS, familiarizing yourself with basic database concepts, and learning how to create, manipulate, and query databases, you are well on your way to becoming proficient in data management.
As you continue your journey, consider exploring more advanced topics such as database normalization, indexing, and transaction management. The world of data management is vast and full of opportunities, and mastering DBMS will undoubtedly enhance your skills as a developer or data professional.
With practice and experimentation, you’ll unlock the full potential of DBMS and transform the way you work with data. Happy database management!
0 notes
Text
Mobile Number Tracker Free: Track Real-Time Location Easily

Advanced tracking technology has made it possible to make sure that dear ones are safe and to locate lost or stolen devices in this digital age. Now, with free mobile number tracker tools available, anyone can track real-time locations with absolute ease. Parents may want to keep an eye on their child, someone may just be trying to locate or recover a phone lost by accident, or a professional might want to ensure the safety of field teams: these tools are useful for all. Let us see how you can make use of mobile number tracker free and an IMEI phone tracker.
Why Use a Mobile Number Tracker?
Mobile number tracker free software helps trace an actual location of the cell phone within real-time. This is particularly useful when:
The parents are interested in keeping tabs on where their children may be.
Employers are to trace their field staff.
Users are trying to trace a lost mobile device for either malicious or good intent.
Concerned relatives are tracking an elderly family member.
In contrast with traditional GPS tracker, mobile number tracker uses a combination of GPS, network towers, and internet data to provide location accuracy.
What is IMEI Number Tracking?
IMEI, standing for International Mobile Equipment Identity, is a 15-digit code being assigned to each mobile device. Through IMEI Number tracking, users have the capability to trace and block devices in case their SIM card has been changed. It is one of the strongest options for finding any lost or stolen smartphone.
Advantages of IMEI Tracking:
Track phone location in the absence of an operational SIM.
Aid law enforcement agencies in retrieving stolen phones.
Remote locking or wiping of phone data.
Thus, an IMEI phone tracking option establishes more security and recovery on your end for a mobile device.
How to Use a Mobile Number Tracker and IMEI Phone Tracker
One of the most trusted online sources for mobile device tracking is TrackIMEI.net. The online service opened up an easy chance for users to perform IMEI number tracking and trace a phone through its number.
Directions:
Step 1: Visit Website: Go to the website TrackIMEI.net.
Step 2: Choose Your Service: Choose whether you want to use mobile number location tracker or do IMEI number tracking.
Step 3: Enter Details: Enter the mobile number or IMEI code for the device you want to track.
Location Tracking: Within a few seconds, a live location of the given mobile device will be displayed on an interactive map.Conversely, this is a simple, efficient, and trustworthy way to continue to be informed and safe.
When to Use IMEI Phone Tracker
Lost Device: If your mobile is lost or stolen, inputting the IMEI code can help in quick retrieval.
Tracking without SIM: In case of SIM card replacement, you can search the phone through IMEI.
Phone management: IMEI tracking could help work businesses that manage several phones in the undertaking of asset control.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
It is important you track these devices ethically and with permission. Legal consequences may follow if attempted without consent.
Closing Thoughts
With free mobile number tracking, IMEI number tracking, and an IMEI phone tracker, mobile tracking is made very easy and effective. And TrackIMEI.net does so through a secure and user-friendly platform that will help you find anyone anytime. Whether for safety, security, or recovery, understanding and correctly using these tools can save you time, money, and stress.
Connect, inform, and keep safe.
Read More : https://trackimei.net/
0 notes
Text
What Innovations Are Shaping the Future of Fintech Platforms?

The fintech industry is transforming at an unprecedented pace, fueled by advancements in technology and evolving customer expectations. From mobile wallets to blockchain-based lending, innovations in fintech software development are not only improving financial accessibility but also redefining how consumers and businesses interact with financial systems. As the demand for seamless, secure, and efficient fintech services grows, several key innovations are emerging as game-changers in the development of future-ready fintech platforms.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are at the forefront of modern fintech innovation. These technologies are being integrated into fintech platforms to enhance personalization, detect fraud, automate financial advice, and improve decision-making. For instance, robo-advisors powered by AI analyze user behavior and risk appetite to offer tailored investment strategies. ML algorithms are also vital in credit scoring, where they assess a borrower’s creditworthiness beyond traditional credit scores by analyzing alternative data sources. In the realm of fintech software development, incorporating AI not only improves user engagement but also enhances operational efficiency.
2. Blockchain and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way data is stored, verified, and exchanged in financial transactions. By ensuring transparency, immutability, and decentralization, blockchain enables secure peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms leverage smart contracts to provide services like lending, borrowing, and trading in a trustless environment. These innovations are reshaping traditional banking models and pushing fintech platforms towards more open and inclusive systems. For developers, blockchain introduces new paradigms in fintech software development, including tokenization, digital identity verification, and decentralized exchanges.
3. Open Banking and API Integrations
Open banking is redefining how banks and third-party providers collaborate. Through secure API integrations, fintech platforms can access user data (with consent) from multiple banks to offer consolidated services such as budgeting, credit comparisons, or personalized offers. This approach promotes competition and innovation in the financial sector. API-driven architecture is now a cornerstone of fintech services, allowing seamless interoperability between different financial institutions and service providers. It also supports faster onboarding, real-time transactions, and integration with external platforms like e-commerce or insurance.
4. Cloud Computing and SaaS Models
Cloud technology has become essential in fintech software development for its scalability, cost-efficiency, and flexibility. Fintech startups and enterprises alike are leveraging cloud-based platforms to deploy and manage applications in real time. The Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model allows companies to deliver financial solutions on a subscription basis, enabling quicker time-to-market and lower infrastructure costs. Cloud-native fintech platforms benefit from better disaster recovery, real-time analytics, and easier maintenance. This trend is driving digital transformation across the fintech landscape.
5. Biometric Authentication and Enhanced Cybersecurity
With increasing digital transactions, security remains a top concern. Innovations in biometric authentication—such as fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and voice identification—are improving the safety and user experience of fintech platforms. In parallel, cybersecurity technologies such as behavioral biometrics, end-to-end encryption, and secure coding practices are being embedded into fintech software development to prevent fraud and data breaches. Strong security frameworks help build user trust, which is essential for the growth of any fintech solution.
6. Embedded Finance
Embedded finance is an emerging innovation that integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms. For example, e-commerce websites offering buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) services or ride-sharing apps providing micro-insurance. By embedding fintech services within daily-use applications, companies can deliver seamless financial experiences without requiring users to visit traditional banks or separate platforms. This trend is expected to drive significant growth in fintech adoption, particularly in sectors like retail, logistics, and healthcare.
7. Real-Time Payments and Digital Currencies
Real-time payment systems are transforming the speed and efficiency of financial transactions. Whether it’s peer-to-peer transfers or instant settlements for businesses, real-time payments improve cash flow and user satisfaction. In addition, the rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and stablecoins is setting the stage for new monetary ecosystems. These digital currencies can be integrated into fintech platforms to provide faster, more secure, and low-cost cross-border transactions. For developers, supporting multiple currencies and payment channels is becoming a crucial aspect of fintech software development.
8. Data Analytics and Predictive Insights
The use of big data and predictive analytics enables fintech platforms to offer smarter, data-driven services. From risk assessment to customer behavior analysis, analytics tools are guiding strategic decisions and personalizing user journeys. Fintech firms that harness data effectively can optimize marketing campaigns, reduce operational costs, and uncover new revenue streams. Predictive analytics is particularly useful in fraud detection, financial planning, and dynamic pricing of financial products.
Conclusion
The future of fintech platforms is being shaped by a confluence of groundbreaking technologies and consumer-centric innovations. From AI-powered personalization to blockchain-based security, these advancements are laying the foundation for more inclusive, efficient, and transparent financial systems. As the industry evolves, embracing these innovations becomes crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Xettle Technologies, a growing player in the fintech ecosystem, is at the forefront of integrating these transformative technologies into real-world solutions. By leveraging cutting-edge tools and staying agile, Xettle Technologies continues to deliver next-generation fintech services designed to meet the dynamic needs of modern users.
In a rapidly changing digital economy, innovation in fintech software development is not just an advantage—it’s a necessity. Platforms that adapt and evolve with these innovations will shape the financial future of tomorrow.
0 notes
Text
The Unseen Power of Linux System Infrastructure: Beyond the Conventional Wisdom
Introduction: Not Just Another Server
When people talk about Linux servers, the conversation often revolves around the obvious. They mention reliability, open-source flexibility, security, and cost-efficiency. But the true essence of Linux servers goes far deeper than just technical specifications and traditional arguments. To understand Linux servers is to understand a philosophy, a movement, and a way of rethinking digital sovereignty. It's not just about running code; it's about choosing freedom, performance, and evolution.
A Living, Breathing Ecosystem
Unlike static operating systems that are updated occasionally by monolithic corporations, Linux servers are part of a vibrant, dynamic, and self-healing ecosystem. Each distribution is a living entity, shaped by communities across the globe, evolving with the needs of real users, developers, and businesses. It is not just software installed on a machine; it is a living organism constantly adapting, optimizing, and innovating. Linux servers do not wait for permission from a central authority to grow; they evolve organically, driven by necessity and passion.
The Philosophy of Choice and Control
Linux servers offer a depth of customization and control that no proprietary system can match. Every decision, from the kernel level to the user space, is yours to make. It forces you to engage with your infrastructure on a deeper level. This engagement creates a symbiotic relationship between the user and the machine. Running a Linux server is not merely about deploying an application; it's about architecting an environment tailored to your precise needs. This level of granular control cultivates a mindset of precision, intentionality, and mastery.
Security Through Transparency
While other systems rely heavily on obscurity and corporate security teams, Linux servers achieve unparalleled security through radical transparency. Every line of code is available for inspection, every vulnerability can be scrutinized by thousands of independent eyes. This isn't just about patching CVEs faster; it's about creating a fundamentally more secure environment through collective vigilance. A Linux server is not a black box; it’s an open book written in real-time by the world’s finest minds.
Resilience in the Face of Adversity
There is a reason why the world’s most critical infrastructure — from financial markets to space exploration — trusts Linux servers. It’s not just about uptime; it’s about resilience. When chaos hits, when unexpected failures cascade, Linux servers offer the kind of composure and recoverability that closed systems simply cannot. Thanks to tools like system snapshots, redundant configurations, and scriptable recovery processes, Linux servers embody a philosophy of survival, adaptability, and engineering for the worst-case scenario.
The True Cost of Ownership
It's easy to highlight that Linux is "free," but that's a shallow way to view its economic advantage. The true cost of a server lies in maintenance, downtime, scalability, and flexibility over time. Linux servers win because they minimize these hidden costs. Their modularity means you can optimize precisely what you need, without paying for bloated software features. Their massive global community means faster troubleshooting and innovation. In the long run, Linux servers don’t just save money — they enable you to reinvest in growth rather than firefighting.
Empowering Innovation and Experimentation
A Linux server is not just a platform for hosting websites or applications. It is a playground for innovation. Want to build a Kubernetes cluster from scratch? Set up a cutting-edge AI environment? Automate complex data pipelines? With Linux, the only limit is your ambition. The open nature of the ecosystem encourages experimentation without penalty. Mistakes are learning opportunities, not costly failures. Every reboot, every configuration tweak, every successful deployment turns you from a consumer of technology into a creator.
The Silent Backbone of the Internet
Every day, billions of people interact with Linux servers without even knowing it. They browse websites, stream videos, communicate across continents — all thanks to infrastructures powered invisibly by Linux. It's the silent workhorse that holds up the modern digital world. Even companies that build proprietary platforms often rely on Linux servers at their core. They don't advertise it, but behind every major cloud provider, every massive database, every seamless user experience, there is likely a Linux box humming quietly in a data center.
Cultural Movement, Not Just Technology
To run Linux servers is to align yourself with a culture that values openness, community, and empowerment. This is a culture that believes in giving back, in documenting knowledge, in challenging monopolies, and in pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Using Linux is not just a technical choice; it is a philosophical one. It says that you value collaboration over competition, transparency over secrecy, and innovation over stagnation.
From Hobbyist to Enterprise: A Universal Language
What’s fascinating about Linux servers rackset is their universal appeal. A teenager learning to code in their bedroom and a Fortune 500 company building multi-region high-availability clusters are both speaking the same language. The barrier to entry is low, but the ceiling for growth is limitless. You can start with a simple VPS and end up architecting complex, distributed systems that span continents — all within the same ecosystem. Linux grows with you, matching your pace, your curiosity, and your ambition.
Future-Proofing Your Career and Your Business
Betting on Linux is betting on the future. With the explosion of cloud computing, DevOps, AI, blockchain, and edge computing, Linux expertise is becoming not just valuable but essential. Businesses that invest in Linux-based infrastructures future-proof themselves against technological obsolescence. Professionals who master Linux servers position themselves at the bleeding edge of innovation, equipped to handle the next generation of technological challenges with confidence.
Conclusion: The Choice That Defines You
Choosing to run Linux servers is not just a technical decision. It is a declaration of independence, a commitment to mastery, a vote for a better digital world. It is a journey from user to creator, from consumer to architect. In a world increasingly defined by opaque systems and centralized control, Linux servers offer a rare gift: transparency, autonomy, and limitless potential. To choose Linux is to choose to stand on the shoulders of giants — and to build something even greater.
0 notes
Text
What Steps Should I Take for OpenEMR Installation Issues?
Introduction
The installation process of OpenEMR presents difficulties due to its power as an open-source Electronic Medical Records (EMR) system. The following section presents known OpenEMR installation issues with corresponding step-by-step solutions.
Common Installation Errors and Solutions
1.PHP Compatibility Issues
Error: OpenEMR installation fails due to compatibility issues with PHP version.
Solution: The installation process requires using PHP version 7.4 or newer versions. The php.ini file requires PHP configuration updates that match OpenEMR settings. Proper error prevention involves enabling Off for short_open_tag while setting the memory_limit to 512M in your php.ini file.
2.Database Connection Failure
Error: “Cannot connect to the MySQL database.”
Cause: This error arises when the OpenEMR installer cannot establish a connection to the MySQL database.
Solution:
· Ensure the MySQL service is running: sudo service mysql start.
· Verify that the credentials in the sqlconf.php file are correct:
Php: $host = 'localhost'; $port = '3306'; $login = 'your_username'; $pass = 'your_password'; $dbase = 'openemr';
3. Blank Page After Installation
Error: A blank screen is displayed after installing OpenEMR.
Cause: Typically caused by a missing PHP module or a permissions issue.
Solution:
· Check for missing PHP modules using php -m | grep -i <missing_module>.
· Install missing modules with sudo apt-get install php-<module_name>.
· Ensure correct file permissions: sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/openemr.
4. Locale Errors
Error: “PHP Warning: Failed to setlocale…”
Cause: The locale settings on the server are not configured correctly.
Solution:
· Install the appropriate locales: sudo locale-gen en_US.UTF-8.
· Reconfigure locales: sudo dpkg-reconfigure locales.
5. SQL Error in OpenEMR Usage
Error: A fatal error occurred that showed “Uncaught Error: SQLSTATE[42S02]: Base table or view not found…”
Cause: The missing database table or improper database table creation process causes this error to appear.
Solution:
· Re-execute the SQL upgrade script through the command: mysql -u root -p openemr < sql/upgrade.sql.
· All database tables need to be imported correctly.
6. PDF Generation Failure
Error: The error message reads, “FPDF error: Unable to create output file.”
Cause: The file system write permissions create a cause that prevents OpenEMR from generating output files.
Solution:
· Users need write permissions in the sites/default/documents directory because of this command: sudo chmod -R777/var/www/openemr/sites/default/documents.
Common Mistakes During Setup
1.Inadequate System Requirements Assessment
· Performance problems emerge because organizations underestimate their hardware requirements along with their software needs.
· System requirements assessment needs to become a complete process done before any installation begins.
2.Neglecting Data Backup and Recovery Planning
· Failing to plan backup procedures and recovery strategies remains one of the main setup challenges.
· Planning for data backup becomes essential since the absence of planning may cause complete loss of information.
· Regular backups should be conducted either through OpenEMR’s tools or third-party scripting solutions.
3.Improper Configuration
· Incorrectly implemented settings result in both performance issues and system errors.
· Users should verify that both database and PHP settings align correctly with OpenEMR’s necessary requirements.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Cloud Success Story: Through OpenEMR Cloud on AWS, this Vermont clinic cut their server maintenance expenses by 70% and also gained better peak-season system capabilities.
On-Premises Example: A large Texas hospital chose on-premises deployment of OpenEMR to sustain whole authority over security standards while maintaining easy integration with current hospital information infrastructure.
Troubleshooting Tips for Windows Installation
· Check PHP settings because you must enable all required PHP extensions while following the correct settings in the php.ini configuration file.
· Check MySQL Connection by verifying the correct running of MySQL and sqlconf.php credentials.
· During installation, use a temporary disable of antivirus software to prevent interruptions.
· You should check OpenEMR directory permissions to stop unauthorized access to its files.
Future Trends in OpenEMR
OpenEMR will continue integrating modern features into its system as healthcare technology advances forward.
AI and Machine Learning
· OpenEMR will incorporate artificial intelligence-based clinical decision support systems and predictive analytics technology for patient care in future updates.
Telehealth Enhancements
· The telehealth system will receive updated modules that enable remote consultation access while offering better healthcare access to patients.
Interoperability Standards
· Additional FHIR technology support in the system will help different healthcare systems communicate their data more efficiently.
Conclusion
The resolution of OpenEMR installation problems requires a careful approach together with expertise in frequent installation barriers. Healthcare providers who focus on PHP compatibility along with database connections and permissions will establish a successful OpenEMR setup while maximizing its functionality. Continuous updates about the latest OpenEMR advancements enable healthcare professionals to achieve maximum performance and efficiency for their management tasks.
FAQs
What are the most common installation errors in OpenEMR?
During OpenEMR installation, you might encounter three major issues that include PHP version conflicts as well as database connection problems and unexplained blank pages showing up because of either missing components or access permission problems.
How do I troubleshoot a blank page error after OpenEMR installation?
Review both PHP module's presence and verify correct permissions for the OpenEMR directory files.
What are some common mistakes during OpenEMR setup?
The integration of insufficient system assessment with poor data backup and recovery planning along with unsuitable configuration represents the main mistakes that cause performance degradation and data loss.
0 notes
Text
The Evolving Job Landscape: Exploring Career Opportunities in Manila
Manila, the bustling capital of the Philippines, continues to be a premier destination for job seekers across the country and beyond. With its dynamic economy and diverse business landscape, the job market in Manila offers a wide spectrum of opportunities spanning traditional industries to emerging sectors. Whether you're a seasoned professional or a fresh graduate, understanding the current job hiring in Manila can help position you for success in this competitive market.
Manila's Economic Resurgence
The post-pandemic economic recovery has accelerated the pace of job opening in Manila, with businesses expanding their operations and new companies establishing their presence in the metropolis. This resurgence has created a favorable environment for job seekers, with increased demand for talent across multiple sectors. From finance and retail to technology and hospitality, jobs in Manila are becoming increasingly diverse, reflecting the city's growing status as a global business hub.
Industry experts note that companies are not just filling vacancies but are actively creating new positions to support their growth strategies. This trend has led to a more dynamic job market, where opportunities exist not only for experienced professionals but also for those looking to transition into new career paths.
The Rise of Remote Work Opportunities
Perhaps one of the most significant shifts in the employment landscape has been the normalization of flexible work arrangements. Work from home jobs in Metro Manila has seen exponential growth, with companies recognizing the benefits of remote work for both employers and employees. Technology firms, BPO companies, and digital marketing agencies are at the forefront of this trend, offering numerous remote positions that provide flexibility without compromising career growth.
These remote opportunities have expanded the geographic reach of Manila-based companies, allowing them to tap into talent pools beyond the metropolitan area while giving professionals the chance to work for prestigious organizations without enduring the notorious Manila traffic. Virtual assistants, content writers, software developers, and customer service representatives are among the most sought-after remote roles in the current market.
Metro Manila's Corporate Landscape
The traditional corporate sector continues to be a significant source of employment, with job hiring in Metro Manila concentrated in business districts like Makati, Bonifacio Global City, and Ortigas. Financial institutions, multinational corporations, and consulting firms regularly announce openings for positions ranging from entry-level associates to senior executives.
What sets these corporate opportunities apart is the emphasis on professional development and career advancement. Many organizations offer structured training programs, mentorship initiatives, and clear progression paths, making them attractive options for ambitious professionals looking to build long-term careers. Additionally, the competitive salary packages and comprehensive benefits associated with these roles continue to draw talent from across the country.
Emerging Sectors and Specialized Roles
As Manila's economy evolves, new sectors are emerging as significant employers. The tech industry, in particular, has seen remarkable growth, with startups and established tech companies alike contributing to the increasing number of job openings in Manila. Data scientists, UX designers, digital marketers, and artificial intelligence specialists are in high demand as businesses embrace digital transformation.
Similarly, the sustainable development sector has gained momentum, with renewable energy companies, environmental consultancies, and green technology firms actively hiring in Manila. These organizations offer professionals the opportunity to apply their skills to meaningful work that addresses pressing environmental challenges while advancing their careers.
Navigating the Job Market
For job seekers looking to capitalize on the opportunities available, staying informed about job hiring trends in Metro Manila is essential. Online job platforms, professional networking sites, and industry-specific forums regularly feature listings for jobs in Manila across various sectors and experience levels.
Additionally, developing in-demand skills through continuous learning and professional development can significantly enhance job prospects. Digital literacy, data analysis, project management, and effective communication are among the competencies highly valued by employers across industries.
The Future of Work in Manila
As we look ahead, the job market in Manila is likely to continue its evolution, with increasing emphasis on digital skills, adaptability, and innovation. The blend of traditional office-based roles and work from home jobs in Manila will likely persist, giving professionals more options in shaping their career paths.
For those currently exploring job hiring in Manila, the diverse opportunities available present both exciting possibilities and the challenge of making informed choices. By staying attuned to industry trends, continuously developing relevant skills, and leveraging professional networks, job seekers can position themselves advantageously in this dynamic market.
Whether you're drawn to the corporate environment of Metro Manila's business districts, the flexibility of remote work, or the innovation of emerging sectors, Manila's job landscape offers something for virtually every professional aspiration.
#jobsinManila #careerinMetromanila #Jobsinmetromanila
0 notes
Text
Database Management System (DBMS) Development

Databases are at the heart of almost every software system. Whether it's a social media app, e-commerce platform, or business software, data must be stored, retrieved, and managed efficiently. A Database Management System (DBMS) is software designed to handle these tasks. In this post, we’ll explore how DBMSs are developed and what you need to know as a developer.
What is a DBMS?
A Database Management System is software that provides an interface for users and applications to interact with data. It supports operations like CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete), query processing, concurrency control, and data integrity.
Types of DBMS
Relational DBMS (RDBMS): Organizes data into tables. Examples: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle.
NoSQL DBMS: Used for non-relational or schema-less data. Examples: MongoDB, Cassandra, CouchDB.
In-Memory DBMS: Optimized for speed, storing data in RAM. Examples: Redis, Memcached.
Distributed DBMS: Handles data across multiple nodes or locations. Examples: Apache Cassandra, Google Spanner.
Core Components of a DBMS
Query Processor: Interprets SQL queries and converts them to low-level instructions.
Storage Engine: Manages how data is stored and retrieved on disk or memory.
Transaction Manager: Ensures consistency and handles ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability).
Concurrency Control: Manages simultaneous transactions safely.
Buffer Manager: Manages data caching between memory and disk.
Indexing System: Enhances data retrieval speed.
Languages Used in DBMS Development
C/C++: For low-level operations and high-performance components.
Rust: Increasingly popular due to safety and concurrency features.
Python: Used for prototyping or scripting.
Go: Ideal for building scalable and concurrent systems.
Example: Building a Simple Key-Value Store in Python
class KeyValueDB: def __init__(self): self.store = {} def insert(self, key, value): self.store[key] = value def get(self, key): return self.store.get(key) def delete(self, key): if key in self.store: del self.store[key] db = KeyValueDB() db.insert('name', 'Alice') print(db.get('name')) # Output: Alice
Challenges in DBMS Development
Efficient query parsing and execution
Data consistency and concurrency issues
Crash recovery and durability
Scalability for large data volumes
Security and user access control
Popular Open Source DBMS Projects to Study
SQLite: Lightweight and embedded relational DBMS.
PostgreSQL: Full-featured, open-source RDBMS with advanced functionality.
LevelDB: High-performance key-value store from Google.
RethinkDB: Real-time NoSQL database.
Conclusion
Understanding how DBMSs work internally is not only intellectually rewarding but also extremely useful for optimizing application performance and managing data. Whether you're designing your own lightweight DBMS or just exploring how your favorite database works, these fundamentals will guide you in the right direction.
0 notes
Text
🚀 Why You Should Choose "Enterprise Kubernetes Storage with Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation (DO370)" for Your Next Career Move
In today’s cloud-native world, Kubernetes is the gold standard for container orchestration. But when it comes to managing persistent storage for stateful applications, things get complex — fast. This is where Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation (ODF) comes in, providing a unified and enterprise-ready solution to handle storage seamlessly in Kubernetes environments.
If you’re looking to sharpen your Kubernetes expertise and step into the future of cloud-native storage, the DO370 course – Enterprise Kubernetes Storage with Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation is your gateway.
🎯 Why Take the DO370 Course?
Here’s what makes DO370 not just another certification, but a career-defining move:
1. Master Stateful Workloads in OpenShift
Stateless applications are easy to deploy, but real-world applications often need persistent storage — think databases, logging systems, and message queues. DO370 teaches you how to:
Deploy and manage OpenShift Data Foundation.
Use block, file, and object storage in a cloud-native way.
Handle backup, disaster recovery, and replication with confidence.
2. Hands-On Experience with Real-World Use Cases
This is a lab-heavy course. You won’t just learn theory — you'll work with scenarios like deploying storage for Jenkins, MongoDB, PostgreSQL, and more. You'll also learn how to scale and monitor ODF clusters for production-ready deployments.
3. Leverage the Power of Ceph and NooBaa
Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation is built on Ceph and NooBaa. Understanding these technologies means you’re not only skilled in OpenShift storage but also in some of the most sought-after open-source storage technologies in the market.
💡 Career Growth and Opportunities
🔧 DevOps & SRE Engineers
This course bridges the gap between developers and infrastructure teams. As storage becomes software-defined and container-native, DevOps professionals need this skill set to stay ahead.
🧱 Kubernetes & Platform Engineers
Managing platform-level storage at scale is a high-value skill. DO370 gives you the confidence to run stateful applications in production-grade Kubernetes.
☁️ Cloud Architects
If you're designing hybrid or multi-cloud strategies, you’ll learn how ODF integrates across platforms — from bare metal to AWS, Azure, and beyond.
💼 Career Advancement
Red Hat certifications are globally recognized. Completing DO370:
Enhances your Red Hat Certified Architect (RHCA) portfolio.
Adds a high-impact specialization to your résumé.
Boosts your value in organizations adopting OpenShift at scale.
🚀 Future-Proof Your Skills
Organizations are moving fast to adopt cloud-native infrastructure. And with OpenShift being the enterprise Kubernetes leader, having deep knowledge in managing enterprise storage in OpenShift is a game-changer.
As applications evolve, storage will always be a critical component — and skilled professionals will always be in demand.
📘 Final Thoughts
If you're serious about growing your Kubernetes career — especially in enterprise environments — DO370 is a must-have course. It's not just about passing an exam. It's about:
✅ Becoming a cloud-native storage expert ✅ Understanding production-grade OpenShift environments ✅ Standing out in a competitive DevOps/Kubernetes job market
👉 Ready to dive in? Explore DO370 and take your skills — and your career — to the next level.
For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
What Is SRE? A Beginner's Guide to Modern Reliability Engineering
The Evolution of Site Reliability Engineering
Large-scale system management has changed significantly with the rise of Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) Foundation. It started at Google in the early 2000s when software engineers were given the responsibility of using code to solve operations problems. By introducing a software-centric approach to infrastructure management, this change sought to close the gap between development and operations.

Flexible in nature, traditional system administration concentrated on resolving problems after they came up. A proactive, engineering-driven model with a focus on automation, dependability, and performance was introduced by SRE. Teams were able to measure and strike a balance between innovation and system stability thanks to concepts like SLAs, SLOs, and error budgets.
These days, SRE principles are not limited to tech giants. SRE is used by businesses of all sizes to increase uptime, decrease labor, and promote cooperation between the operations and development teams. SRE keeps evolving in response to the growing complexity of systems and the need for resilience; it is essential to the development of scalable, dependable, and effective digital services.
DevOps vs. SRE: What’s the Difference?
1. Origin
DevOps is a cultural movement that emerged to improve collaboration between development and operations.
SRE was created at Google as a way to apply software engineering to operations tasks.
While DevOps evolved as a philosophy to break silos, SRE is a concrete set of practices rooted in engineering discipline.
2. Focus
DevOps emphasizes faster delivery through automation and collaboration.
SRE focuses on ensuring reliability, scalability, and performance.
DevOps is about speed and efficiency; SRE ensures systems stay reliable as they scale.
3. Approach
DevOps promotes practices like CI/CD and Infrastructure as Code.
SRE uses SLAs, SLOs, SLIs, and error budgets to manage risk.
SRE adds measurable, reliability-focused engineering to the DevOps workflow.
4. Roles and Teams
DevOps encourages shared responsibility across teams.
SRE introduces a dedicated role with strong coding and ops skills.
SREs often act as reliability guardians, while DevOps promotes a collaborative environment.
Top Tools Every Site Reliability Engineer Should Know
Site Reliability Engineers (SREs) Training play a critical role in maintaining the reliability and performance of modern systems. To do this effectively, they rely on a robust toolkit that covers monitoring, automation, logging, and infrastructure management.
1. Prometheus – An open-source monitoring system that collects time-series data and provides powerful alerting capabilities. It's often the go-to tool for system health checks.
2. Grafana – Frequently used with Prometheus, Grafana offers rich dashboards and visualization for system metrics, helping teams quickly detect anomalies.
3. ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) – This trio helps with centralized logging and data analysis. SREs use it to search logs, identify root causes, and track trends over time.
4. Chaos Monkey – Developed by Netflix, this chaos engineering tool randomly terminates instances in production to test a system’s resilience and recovery strategy.
5. Kubernetes – A container orchestration platform that automates deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, making it essential for managing complex infrastructure.
6. Terraform – A leading Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool used to automate infrastructure provisioning and ensure consistency across environments.
The Future of SRE
In 2025, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) is adapting to new demands as technology advances. One significant trend is increasing use of AI and machine learning in incident response and observability. SREs use predictive analytics to identify and fix problems before affecting users.
Another shift is the rise of platform engineering, where internal developer platforms (IDPs) streamline infrastructure and reliability practices across teams. SREs are playing a key role in building and maintaining these platforms.
Security and compliance are also becoming core responsibilities, with reliability now extending to areas like zero-trust architecture and data governance.
Additionally, multi-cloud and edge computing environments are challenging SREs to rethink monitoring, automation, and resilience strategies.
SREs are not just problem solvers—they’re strategic partners driving innovation, scalability, and trust in digital systems.Uncover details: Site Reliability Engineering Courses
0 notes
Text
How Online Student Information Management Systems Are Revolutionizing Education
The American education system has undergone a dramatic digital transformation in recent years, with online Student Information Management Systems (SIMS) and Student Management Systems (SMS) leading the charge. These cloud-based SaaS (Software as a Service) platforms have revolutionized how schools operate, creating unprecedented opportunities for efficiency, accessibility, and educational improvement.
The SaaS Revolution in Education Management
Remember the days when student records were stored in filing cabinets, attendance was taken with paper and pencil, and IT departments struggled to maintain clunky on-premises servers? For many American schools, those days are long gone. Today's SaaS-based Student Information Management Systems have moved critical educational data to secure cloud environments, creating powerful advantages for districts of all sizes.
The shift to cloud-based SaaS models has democratized access to sophisticated educational technology. Small rural districts now utilize the same powerful tools as large urban systems without massive upfront investments, leveling the playing field and ensuring all students benefit from modern educational practices.
"Moving to a cloud-based SIM system was a game-changer for our small district," explains Jennifer Lopez, Technology Coordinator at a rural school in Minnesota. "We gained enterprise-level features that were previously only available to much larger schools, and our IT team was freed up to focus on supporting classroom technology instead of maintaining servers."
The Power of SaaS for School Operations
SaaS-based student management systems have transformed the economics of school technology:
Subscription-Based Pricing: Instead of large capital expenditures every few years, districts can budget for predictable monthly or annual subscription costs.
Reduced Infrastructure Costs: Cloud-based systems eliminate the need for expensive on-premises servers, specialized cooling systems, and redundant power supplies.
Automatic Updates: Gone are the disruptive weekend and summer upgrade cycles—SaaS solutions update automatically, often without any downtime.
Scalability: Systems grow seamlessly with your district, whether you're adding five students or five schools.
Business Continuity: Cloud-based solutions offer built-in disaster recovery, ensuring access to critical student information even if local facilities are compromised.
Within this SaaS landscape, some providers have adapted open-source platforms like openSIS to offer cloud-hosted versions, combining the flexibility of open-source with the convenience of SaaS delivery.
Real-Time Access: Connecting School Communities Like Never Before
Perhaps the most transformative aspect of SaaS-based Student Management Systems is their ability to connect educational stakeholders in real time. Parents no longer need to wait for report cards or parent-teacher conferences to understand how their child is performing. Instead, they can log in any time to view grades, attendance, assignment completion, and teacher communications.
I recently spoke with Maria Sanchez, a high school principal in Arizona, who shared, "Our online system has completely transformed parent engagement. We've seen attendance improve and assignment completion rates increase because students know their parents have instant access to this information."
Breaking Down Geographic Barriers
The pandemic accelerated adoption of cloud-based systems, but their benefits extend far beyond emergency remote learning scenarios. Today's mobile-friendly SaaS platforms mean that:
Military families can maintain consistent access to their children's educational records despite frequent relocations
Parents who travel for work can stay connected to their children's education from anywhere with internet access
Students who are homebound due to illness can remain engaged with their educational community
Teachers can review student data and plan lessons whether they're in the classroom or at home
Enterprise-Grade Security in the Cloud
While the convenience of online systems is undeniable, security concerns remain paramount for educational institutions handling sensitive student information. Modern SaaS-based Student Information Management Systems address these concerns through:
Advanced encryption protocols that protect data both at rest and in transit
Role-based access controls that ensure information is only available to authorized users
Regular security audits and compliance with federal regulations like FERPA
Automated backup systems that prevent data loss
Dedicated security teams monitoring for threats 24/7
Most districts find that reputable SaaS providers offer security capabilities far beyond what they could implement locally, making cloud-based solutions a security upgrade rather than a compromise.
The Financial Case for SaaS Student Management Systems
Budget-conscious school boards across America have found that SaaS models deliver significant financial advantages:
Predictable Budgeting: Subscription-based pricing eliminates surprise costs and allows for more accurate long-term financial planning.
Reduced Staffing Requirements: Districts can operate with leaner IT departments when they're not managing complex on-premises systems.
Elimination of Hardware Refresh Cycles: The costly 3-5 year server replacement cycle disappears with cloud-based solutions.
Pay-for-What-You-Use Pricing: Many SaaS providers offer tiered pricing based on actual usage, allowing districts to scale costs with their needs.
Some providers have taken this financial advantage even further by offering cloud-hosted versions of open-source platforms like openSIS, combining the cost benefits of open-source software with the convenience of SaaS delivery.
Looking Ahead: The Next Generation of SaaS Education Tools
As these systems continue to evolve, we're seeing exciting innovations that will further transform American education:
AI-powered early warning systems that identify students at risk of falling behind
Advanced analytics that help districts identify educational trends and optimize resource allocation
Integrated communication tools that automatically translate messages for non-English speaking families
Personalized learning dashboards that empower students to take ownership of their educational journey
Hybrid approaches that combine the best aspects of commercial SaaS and open-source flexibility
For American schools looking to prepare students for an increasingly digital world, implementing a cloud-based SaaS Student Information Management System isn't just a technological upgrade—it's an essential step toward educational excellence in the 21st century. Whether through pure SaaS products or cloud-hosted open-source alternatives like openSIS, the path to digital transformation has never been more accessible.
0 notes
Text
Real-Time Data Streaming: How Apache Kafka is Changing the Game
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital world, real-time data streaming has become more essential than ever because businesses now rely on instant data processing to make data-driven and informed decision-making. Apache Kafka, i.e., a distributed streaming platform for handling data in real time, is at the heart of this revolution. Whether you are an Apache Kafka developer or exploring Apache Kafka on AWS, this emerging technology can change the game of managing data streams. Let’s dive deep and understand how exactly Apache Kafka is changing the game.
Rise of Real-Time Data Streaming
The vast amount of data with businesses in the modern world has created a need for systems to process and analyze as it is produced. This amount of data has emerged due to the interconnections of business with other devices like social media, IoT, and cloud computing. Real-time data streaming enables businesses to use that data to unlock vast business opportunities and act accordingly.
However, traditional methods fall short here and are no longer sufficient for organizations that need real-time data insights for data-driven decision-making. Real-time data streaming requires a continuous flow of data from sources to the final destinations, allowing systems to analyze that information in less than milliseconds and generate data-driven patterns. However, building a scalable, reliable, and efficient real-time data streaming system is no small feat. This is where Apache Kafka comes into play.
About Apache Kafka
Apache Kafka is an open-source distributed event streaming platform that can handle large real-time data volumes. It is an open-source platform developed by the Apache Software Foundation. LinkedIn initially introduced the platform; later, in 2011, it became open-source.
Apache Kafka creates data pipelines and systems to manage massive volumes of data. It is designed to manage low-latency, high-throughput data streams. Kafka allows for the injection, processing, and storage of real-time data in a scalable and fault-tolerant way.
Kafka uses a publish-subscribe method in which:
Data (events/messages) are published to Kafka topics by producers.
Consumers read and process data from these subjects.
The servers that oversee Kafka's message dissemination are known as brokers.
ZooKeeper facilitates the management of Kafka's leader election and cluster metadata.
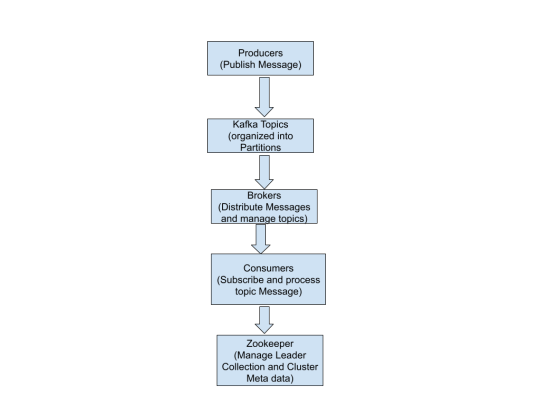
With its distributed architecture, fault tolerance, and scalability, Kafka is a reliable backbone for real-time data streaming and event-driven applications, ensuring seamless data flow across systems.
Why Apache Kafka Is A Game Changer
Real-time data processing helps organizations collect, process, and even deliver the data as it is generated while immediately ensuring the utmost insights and actions. Let’s understand the reasons why Kafka stands out in the competitive business world:
Real-Time Data Processing
Organizations generate vast amounts of data due to their interconnection with social media, IoT, the cloud, and more. This has raised the need for systems and tools that can react instantly and provide timely results. Kafka is a game-changer in this regard. It helps organizations use that data to track user behavior and take action accordingly.
Scalability and Fault Tolerance
Kafka's distributed architecture guarantees data availability and dependability even in the case of network or hardware failures. It is a reliable solution for mission-critical applications because it ensures data durability and recovery through replication and persistent storage.
Easy Integration
Kafka seamlessly connects with a variety of systems, such as databases, analytics platforms, and cloud services. Its ability to integrate effortlessly with these tools makes it an ideal solution for constructing sophisticated data pipelines.
Less Costly Solution
Kafka helps in reducing the cost of data processing and analyzing efficiently and ensures high performance of the businesses. By handling large volumes of data, Kafka also enhances scalability and reliability across distributed systems.
Apache Kafka on AWS: Unlocking Cloud Potential
Using Apache Kafka on ASW has recently become more popular because of the cloud’s advantages, like scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency. Here, Kafka can be deployed in a number of ways, such as:
Amazon MSK (Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka): A fully managed service helps to make the deployment and management of Kafka very easy. Additionally, it handles infrastructure provisioning, scaling, and even maintenance and allows Apache Kafka developers to focus on building applications.
Self-Managed Kafka on EC2: This is apt for organizations that prefer full control of their Kafka clusters, as AWS EC2 provides the flexibility to deploy and manage Kafka instances.
The benefits of Apache Kafka on ASW are as follows:
Easy scaling of Kafka clusters as per the demand.
Ensures high availability and enables disaster recovery
Less costly because it uses a pay-as-you-go pricing model
The Future of Apache Kafka
Kafka’s role in the technology ecosystem will definitely grow with the increase in the demand for real-time data processing. Innovations like Kafka Streams and Kafka Connect are already expanding the role of Kafka and making real-time processing quite easy. Moreover, integrations with cloud platforms like AWS continuously drive the industry to adopt Kafka within different industries and expand its role.
Conclusion
Apache Kafka is continuously revolutionizing the organizations of modern times that are handling real-time data streaming and changing the actual game of businesses around the world by providing capabilities like flexibility, scalability, and seamless integration. Whether you are deploying Apache Kafka on AWS or working as an Apache Kafka developer, this technology can offer enormous possibilities for innovation in the digitally enabled business landscape.
Do you want to harness the full potential of your Apache Kafka systems? Look no further than Ksolves, where a team of seasoned Apache Kafka experts and developers stands out as a leading Apache Kafka development company with their client-centric approach and a commitment to excellence. With our extensive experience and expertise, we specialize in offering top-notch solutions tailored to your needs.
Do not let your data streams go untapped. Partner with leading partners like Ksolves today!
Visit Ksolves and get started!
#kafka apache#apache kafka on aws#apache kafka developer#apache cassandra consulting#certified developer for apache kafka
0 notes